- View 3644
- INQUIRIES : (International) 02-2112-5503 / en_healthcare@snuh.org (English consultation available)
- LOCATION : Yeoksam-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul
- ADDRESS : 38-39F, Gangnam Finance Center, 152, Teheran-ro, Gangnam-gu
CPR Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation 4 Minutes of Life-Saving Miracles [SEOUL NATIONAL UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL GANGNAM CENTER]

“Will it happen around me? Will I have to perform CPR?”
Being prepared to administer CPR is crucial for bystanders until paramedics arrive, significantly increasing the chances of survival. Timely and effective CPR can save a life within 4 minutes of cardiac arrest. CPR training equips individuals to be a lifeline for family and friends.
What exactly is sudden cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation?
Cardiac arrest is a condition in which the heart's pumping function, responsible for blood circulation in the body, suddenly stops due to a various causes. When a heart attack occurs, the blood supply to the body is cut off, eading to the onset of damage to brain cells typically within 4 minutes After 10 minutes, permanent brain damage and organ damage can lead to death. Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation is a first aid method that artificially maintains breathing and circulates blood when breathing or the heart stops beating. When the heart has stopped working, CPR is a method of circulating the blood with external effort, which is crucial for delaying damage to the brain and recovering from a heart attack.
What does the 4-minute miracle mean in CPR?
Because brain cells begin to damage more than four minutes after the heart stops, CPR should be started “immediately if the heart stops or is suspected.”To confirm cardiac arrest, one can check for consciousness and breathing. Performing CPR "as quickly as possible"can significantly increase the chances of survival.

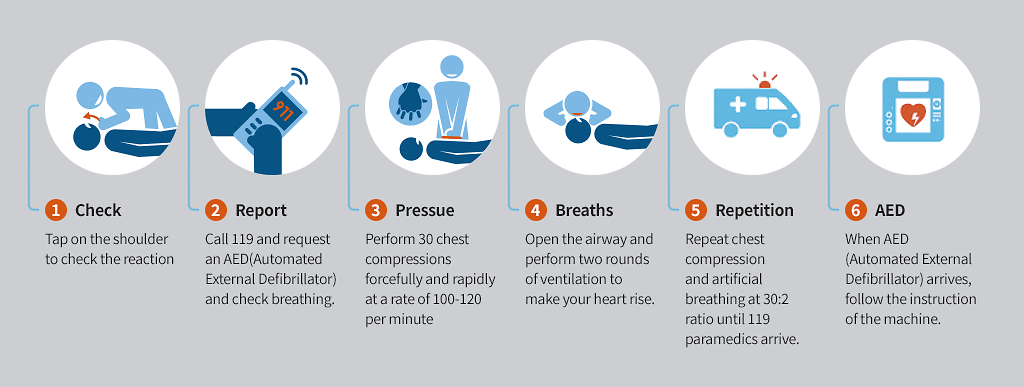
If I am an early witness, how should I perform CPR?
First, check the consciousness. Confirmation of consciousness is done by tapping both shoulders hard and asking, “Are you okay?” You have to ask out loud. If there is no reaction, there is a possibility of cardiac arrest. Second, if you find that there is no response, call 119 immediately by loudly notifying the people around you, and bring an AED(Automated External Defibrillator) if you have one. Even if you don't have CPR experience, you can still do it with the telephone guidance of a 119 paramedic. Third, check their breathing. If you observe the movement of their chest and upper abdomen with your eyes for 10 seconds and they are not breathing or panting, it should be considered apnea. If non-response and apnea are identified, it is cardiac arrest. Fourth, start chest compressions as soon as cardiac arrest is confirmed. After 30 chest compressions, open the airway and perform 2 artificial respirations to allow the chest to rise. However, if it is difficult to maintain the airway and sufficient ventilation is not possible or you are reluctant to give mouth-to-mouth ventilation to others, continue with sufficient speed and intensity of chest compressions. Every 2 minutes, check their response and breathing, and repeat the process of chest compressions again. Fifth, when the AED is ready, attach the pad to the indicated location and press the button to perform defibrillation as instructed by the machine. AEDs are mandatory in apartment complexes with more than 500 units in accordance with Article 47(2) of the Law on Emergency Medical Care. If you don't have an AED, repeat chest compressions until 119 arrives.
Seoul National University Hospital Gangnam Center is a health
checkup center that provides comprehensive and in-depth checkups.